Sulzer on British Railways
In 1954 British Railways had about 6,000 steam locomotives falling apart at the rivets so embarked on a programme to replace these with four classes of mainline locomotives together with some smaller classes of shunting locomotives. Various manufacturers put forward different types of prototypes and very quickly Sulzer won orders for the power units for the Types 2, 3 & 4: these being 6, 8 & 12 cylinder LDA28 engines respectively.
Vickers at Barrow in Furness had geared up in the early 1950s to produce submarine engines in large quantities in anticipation of an escalation of the war in Korea. This never happened but Vickers had a large works ready to make LDA size engines in great quantity with very quick deliveries, a situation that was recognised by certain people on BR and Sulzer's 'father' of Traction - Tom Schur who was head of Dept 8 in Switzerland where various sizes of LDA engine were already being built for other railway companies. Sulzer (London) took a license from Winterthur and apart from the first 10 engines built in Switzerland, Vickers built about 1,500 engines over a period of 5 years - an engine every working day. This Sulzer order represents the largest single customer contract in the history of Sulzer and will probably stand for all time - a fact stated by Peter Sulzer at the funeral of Tom Schur.
I joined Sulzer London in 1966 when the main build programme was nearly complete and even though I was taken on as a Design Liaison Engineer looking after the flow of information and drawings from Winterthur to Barrow, the duties changed very quickly into those supporting development and service. At this juncture, I would mention that every industry I've been involved with - automotive, railway, aeronautical and marine, the equipment is never perfect from the word go; hence BR engineers frequently accused us of using them as mobile test beds for development purposes. The railway industry is probably the most arduous duty for any engine because of its cyclic nature. The drivers had come from a steam world where the regulator was either open or closed depending on the speed and gradient - I always wondered as a boy what those boards at the side of the track meant. When the diesels came along, nothing changed. The Power handles on the control desk were marked 'off', 'on' and 'max', the drivers once under way only moved the handle to either 'on' and 'max' depending on the speed they wished to maintain - they never used intermediate positions. The engine governor was even marked 'stellung regler' - the German for regulator position!
Winterthur designed and fitted an electronic governor on D1880 - a Type 4 locomotive with a 12LDA28C engine which had both Power and Load control facilities. We made a test run from London to Leeds and back in both modes with engine speed recording equipment fitted to register the difference. On the outward run we asked the driver to use his usual procedure in power control, but return on load control - as if on cruise control on a modern road vehicle. He had to persuaded to leave the handle alone except when slowing for signals etc. Back in London he thanked us but swore he would never use this mode again because it made him nervous! The readings from the recorder were very different - the outward trace looked like a saw tooth, whereas the return journey trace was a lot smoother with far less speed changes and therefore less load and thermal cycles on the engine. This cycling imposed huge stresses on all the engine components and led to a process of continual development to increase the time between service intervals and to extend the reliability of the overall power unit. More of this later in the story.
The Sulzer operation in the London office was relatively small in relation to the vast numbers of locomotives coming into service as the main task was to be the communication channel between the specialists in Winterthur and the builders and operators in the UK. At the same time, we had a number of Winterthur engineers working in the London office who acted as on-the-spot liason staff between Sulzer and BR at a senior level. However, it was always envisaged that the London staff would be expected to control the spares and service issues going forward and hence the UK engineers would have to be on a steep learning curve to deal with all the technical issues first hand. The spares operation will be covered later in the story.
In the early years we had about 40 erectors/service personnel at all the engine and locomotive building works such as Vickers Barrow, BR Crewe and Derby, Brush, Beyer Peacock, Darlington and Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon. Service engineers were posted at every BR maintenance depot in the UK running Sulzer engined locomotives; they all reported to the London office and regular meetings were held to update them with service and development issues. The work at Vickers covered the construction, assembly and testing of the complete LDA28 power unit, i.e. with its appropriate generator from Brush, GEC, or Crompton Parkinson - depending on the type of locomotive. Whilst Vickers fabricated the bed plates and cylinder blocks, they also made many of the running gear components and ancilliary items. This left a great number of parts that came from specialist suppliers - many of whom were well known in British industry. The list would be too large to include here but mention must be made of De Havilland (turbochargers), Specialloyd (pistons), Glacier (bearings), Vickers Hydraulics (governors), Holset (vibration dampers), Mitchell Shackleton (crankshafts), Bryce Berger, CAV, Wilson and Kyle (fuel injection pumps), Serck (radiators and coolers) and Sheepbridge Stokes (cylinder liners). In later years, strong relationships with these and other companies were forged through ongoing developments in so many technological fields. At the same time, Winterthur were solidly behind us with their specialist engineers and scientists conducting technical investigations on materials and processes. Examples of this will be covered later under service problems.
Just to enlarge on this aspect, the 12 cylinder LDA double bank engine at it's highest C rating was subject to unacceptable stresses and vibrations in the early years mainly due to the cyclic nature of the service as mentioned above, but partly because of faulty welding techniques at Vickers. It should be remembered that the LDA28 was a late 1930s design but it won large orders based on its high power/weight ratio due to the double bank design, it met the BR delivery requirements and came from a famous company in the railway industry. Indepth technical expertise on diesel traction was thin on the ground within BR - they were very largely steam engineers and therefore the design details and service experience of diesels was all new to them. At the same time in 1954, welding and machining techniques were relatively basic compared to what came along - rapidly, during the course of the initial contract and the very long service period of over 40 years! Knowledge of deep penetration welding was available, but its application to the fabrication of bed plates and cylinder blocks left a lot to be desired. Submerged arc welding and computer controlled machines were also unknown at that time.
Although Vickers welding techniques and quality can be criticised, they were certainly in the forefront in other areas. Having built many ships - both merchant, naval and submarines, they were absolute experts at gearbox manufacture. The double bank 12LDA was two 6 cylinder engines side by side in integral crankcases and cylinder blocks. The two crankshafts transmitted the power by way of gears known as synchronising gears: these connected the two crankshafts to a third gear driving the generator. Vickers had special machinery (MAAG) for hobbing and grinding these gears and they were made in matched sets of three. BR were deeply suspicious of the integrity of the synchronising gears and we were asked to hold 30 sets in stock as spares against future failures. None of these gears were ever needed and eventually BR paid for them at cost price! The overall size of the contract meant that Vickers had to design and built special machines and jigs to build these engines within the promised delivery times. One of these was the boring machine for the 12LDA crankcases and was designed to ensure that all the bearing saddles on both banks were in line with each other.
Winterthur conducted extensive strain gauge investigations on the test bed and introduced the large rebalancing and derating programme to deal with the problem of structural failures in the crankcases and cylinder blocks. This involved returning every 12LDA28C engine to Barrow for some welding modifications and rephasing and balancing of the crankshafts. At the same time, the engines were derated from 2,750 hp at 800 rpm to 2,580 hp at 750 rpm. This considerably improved the reliability of the engines but further stress relief machining work was necessary on the cylinder blocks and crankcases - this was done at the main works of Crewe and Derby. As mentioned above, driving practices didn't change nor did some of the maintenance procedures, consequently Sulzer were kept very busy investigating problems and searching for solutions. I will list a few of these together with the modifications introduced and it may be realised that the LDA28 engine was on a continuous development programme.
Apart from structural problems, the next most troublesome area was the turbocharger. The cyclic running and rapidly changing heat gradients meant that virtually all the components in the turbocharger had to be modified over time. Here again investigations were conducted by many Sulzer departments whose expertise and facilities were always readily available to the Diesel Division. The Research Dept had the latest equipment for testing materials for bearings, piston rings, cylinder liners and particularly exhaust valves. They conducted a series of high temperature strain gauge tests on valve materials which had an influence on all other Sulzer four-stroke engines. The foundry in Oberwinterthur was the most modern in Europe and were vital in helping us overcome various problems with castings and their materials.
• Turbine casing cracking - strain gauge testing by Winterthur led to a change in the internal wall thickness of the casting. Wtr.
• Nozzle ring distortion - change of manufacturing technique from fabricated to precision casting, Wtr
• Gas inlet casing - cracking and distortion - change of material from cast iron to cast steel, Wtr
• Turbine blade - high temperature erosion - change of material and production method - Centrax,
• Turbine wheel - change of production method from broaching to wire spark erosion - Vickers,
• Impellor fracturing from the spline causing major damage inside - and outside, the turbocharger. Change from spline to peg drive - Wtr, British Airways, Wilson & Kyle,
• Cylinder head - cracking across the flame face - change of design and manufacturer, Wtr, Elmec Engineering
• Cylinder liner cracking under the collar - change of design, material and method of manufacture to centrifugal casting, Wtr, Sheepbridge Stokes
• Bearing problems were not severe but advantage was taken in the light of change of materials on other engines, Wtr, Glacier,
• Exhaust valve head fracture - see above re - material change from HT to Austenitic steel, Wtr, Markisches Werk
• Piston ring fracturing - change of material, Wellworthy, Daros
Right from the start, a constant problem was one of keeping fluids in the engine. Joint leakage was always with us - particularly from coolant hoses and bushes. Eventually the Research Dept. of BR built a hose rig at Derby to develop materials and connections to overcome most of the problems. The rubber transition bush which transfered coolant from the cylinder block to the head was redesigned to eliminate this constant irritation and silicon rubber was introduced on this component and on virtually all other hoses and pipe connections. At the same time this material was also used on the crankcase doors to eliminate oil leaks. See note 1 below.
BR set up a Working Group to investigate a series of service problems which were inter-related and Sulzer were naturally involved with this as a permanent member of the Group. The practices laid down in BR working practices meant that the Maintenance Depots were going their own way when it came to servicing fuel injectors. Despite the advice from Sulzer, Wilson & Kyle and Bryce Berger, they insisted on endlessly grinding nozzle bodies even though the case hardening on the seat had worn through to softer steel. They just would not replace the complete nozzle - I fought them on this my whole 12 years in Traction and even some years in Marine! The Depot passed the injectors as fit for service because they were producing a good spray pattern on the rig. The end result was a rapid deterioration in the fuel injection leading to black smoke exhaust, build up of carbon on the piston head and neat unburnt fuel running down the cylinder wall causing premature liner wear and crankcase oil dilution. To add to this catalogue of associated problems, when first designed, the Type 4 batteries were never large enough for repeated cold starts and BR couldn't use anti-freeze because of disposal/ecological restrictions. (Actually, anti-freeze would have added to the leakage issues mentioned above because it is more 'searching'). So BR turned to Borax Sodium Metasilicate water treatment and to combat cold weather and poor batteries, they idled the locomotives when not in service! Put all this together - neat fuel dribbling in at idling speeds causing more oil dilution, cylinder liner glazing due to the oil being washed off, oil carry over into the exhaust system causing fires in the pipes and turbo charger 'hot' components and finally, degradation of the lubricating oil meaning more frequent changes. BR even developed a lubricating oil recovery plant to 'clean' and re-dose used engine oil when all along the simple solution was to renew the injector nozzle at specified service intervals.
Governing
Even though it is every schoolboy's dream to be a train driver because it is noisy and exciting, the job requires a lot of skill and knowledge of the road. However the change from steam to diesel was a culture shock for most people on BR and governing was almost a 'black art' in their minds and hence much training and familiarisation had to be provided by Sulzer. I was nominated as the one to take on this task in the UK and following my own training in Winterthur, I had to pass this on to the operators both in the UK and overseas. We made wooden models of the governor to illustrate how the various linkages and valves worked together to control the fuel injection and load regulator functions. About four times a year it was necessary to attend the BR School of Transport to lecture on all aspects of the LDA28 engine to senior staff from the BR Technical Centre, main works and maintenance depots. Drivers had their own training school and their instructors also attended these lectures from time to time. There were always more questions on governing than anything else; myself and my manager - Arthur Tayler, were kept very busy at this time and it has to be said that it was always difficult to get governor modifications through the BR 'system' because they didn't fully understand how it all worked!
The governors were built by Vickers Hydraulics to an ingenious and complicated Sulzer design which had to match a number of parameters together in order to keep the engine running on its design power curve and they were tested/set on a special rig - copies of which were later built and supplied to Crewe, Derby, Eastleigh and Glasgow - and overseas to Malawi, Mozambique and Nigeria. The governing and control of diesel engines depends on the application - stationary and diesel electric marine engines run at constant speed, whereas a marine engine driving a directly coupled propeller runs according to a fixed propeller curve - depending on the speed required for the ship. A locomotive engine also has a fixed power curve but varies according to load and the position of the power handle as described previously. The parameters mentioned above are speed, power and governor position; on the rig only speed and governor postion can be set according to the figures from the design power curve for that particular engine's rating, e. g. the 12LDA28C had a maximum power of 2,750 hp at 800rpm at a governor position of 8. 9. These figures have been directed by the designers and thermodynamatists following extensive test bed running.
Hence the driver is selecting a governor position and thus a point on that power curve when he moves his power handle. (It was not always possible to exactly achieve these figures because the engine efficiency varied slightly from a new engine to one that was approaching overhaul). The unit is purely hydraulic/mechanical (no electronics on these locomotives) only switches, solenoids, relays and rheostats controlling the DC current to the traction motors. Hence, no sensors or solid state controllers. The governor, apart from responding to instructions from the power handle, can only sense speed in terms of the load on the engine - again depending on gradient and operational requirements of the train. As the governor is driven from the camshaft, it senses this speed through simple flyweights which act as follows on the rest of the system. On starting, first of all an electrically driven triple pump set primes the fuel system, circulates coolant through the engine and pumps oil through the whole system and up to the governor. (This unit is not actually pressurised - in fact testing and setting was done with the top cover off). When the pressure switches reach their set points, the power handle is moved to 'On' and an electrical signal opens a solenoid valve on the governor allowing oil to flow into the internal channels that feed the cylindrical slide valves, piston and servo motor. By means of a linkage to the governor position lever (which is now set at idling), and one of the slide valves, oil pushes on a large piston connected to an output lever which in turn is part of the fuel pump linkage - thus opening the pumps to their idling position. On pressing the 'Start' button, the generator now acts as a motor from the batteries to crank the engine. The engine starts, runs at idling speed and the main pumps maintain the pressures.
When the locomotive is ready to move, the power handle is moved up and another slide valve allows oil to flow into a vane type servo motor which rotates the attached load regulator which controls the field strength of the main generator thus supplying power to the traction motors. Simultaneously, the large piston moves again and opens the fuel racks. The load regulator is a cylindrical internal rheostat i.e. a contact brush runs round the internal commutator where each segment is connected to different windings in the generator thereby switching the fields in and out. As the locomotive gathers speed and less power is required from the engine, the governor senses this rise in engine speed - (through the flyweights) and turns the load regulator to reduce the field strength and at the same time reduces the fuel rack position; if the power handle is left alone the engine will run on this (new) power curve setting.
There are some protection devices built into the governor as follows: -
• electrical failure - the oil input solenoid closes
• loss of oil pressure - the system shuts down
• turbocharger failure - when the air pressure from the turbocharger is normal, a bleed from the inlet manifold acts on a small rubber diaphragm which keeps the oil supply to the slide valves open. If the charge air pressure falls, the governor would shut down to a reduced power level.
The engine overspeed trip is on the other end of the camshaft and consists of a centrifugal weight which will shut down the fuel racks in the event of an overspeed. The governor gave very little trouble apart from the odd failure of the input solenoid and the rubber diaphragm. However it was necessary to modify the main drive arrangement from a dog drive to a spline drive following fatigue failures in the flyweight shaft. However, because of the constant movements of the power handle and the cyclic running as discussed above, three modifications had to be made inside the governor to protect the engine and turbo charger. The oil flow through the slide valves could be rather sudden at times of frequent load changes and this could lead to 'hunting' of the fuel racks, so some aluminium damper sleeves were fitted to slow down the rate of flow through the valve controlling the fuel racks. It was found that a similar problem occured on one of the oil galleries - i.e. the flow needed to be slowed down but only in one direction. This was solved by fitting a sliding bush in the gallery so that the oil flowed freely when the bush was at one end of its travel, whereas at the other end oil had to flow at a lower rate through the orifice in the middle of the bush. See note 2 below. Similarly, if the power handle was suddenly turned back to the 'On' position, i.e. the driver decided to coast for a while, another slide valve would rapidly turn the load regulator back and this combined with the reduction in the fuel setting, could cause the turbo charger to surge because it couldn't get rid of all its charge air instantly. (As an aside, this is why turbo charged race cars have waste gates!). To overcome this problem an adjustable screw was fitted above one of the slide valves - again, to limit its lift when powering down. See note 3 below.
From the beginning of the programme, apart from Erectors/Service Engineers being posted at Works and Depots, a number of senior engineers from Winterthur worked out of the London office as mentioned above and some of them came up with modifications to overcome certain problems. They were all highly skilled and experienced engineers and they gave their names to some of the unusual solutions referred to above.
Note 1: - Cylinder liner upper sealing rings - Bartels
Note 2: - Sliding bush - Inhelder
Note 3: - Adjustable screw: - Spaltenstein (Erector at Crewe Works)
Mention must be made of my colleagues looking after spare parts because although in the first couple of years of the programme the spare gear was ordered from Vickers, Sulzer London had to set up an extensive logistics operation from then on. Norman Lewis led this team and he was responsible for searching out new suppliers in place of those companies that had closed for one reason or another during the rapid de-industrialisation of heavy engineering in Britain. Parts were ordered from literally dozens of manufacturers - from the smallest bolt up to large components such as cylinder liners, so we employed buyers, progress chasers, storemen and inspectors. A large warehouse was full of traction and marine parts and when the whole company moved to Farnborough, an even bigger Stores was built to cope with the half - life overhaul of all 508 LDA28C engines. The traction spares business was the most profitable division of Sulzer UK for nearly 40 years. During my 32 years with Sulzer, the work was never dull and because I had to deal with a huge number of contractors, I got to learn about a vast range of products, services and operators involved with the Railway industry. The latter 20 years gave me similar opportunities and experience in the Marine industry. Throughout my career, it was a priviledge and a pleasure to work with all my colleagues in both the UK and particularly Winterthur, (where following the amalgamation of Traction and Marine into one Diesel Division), I was still dealing with the same staff who were always ready to investigate the service problems coming back from the operators and then patiently explain the mode of failure and the recommended solutions.
After the LDA28 on British Railways
The trial with 12LVA 24 engines in four Type 4 locomotives, the Kestrel locomotive and the subject of the A25 engine for rail traction, was covered in a bulletin dated March 2008. However, following an enquiry from one of my correspondents concerning CCM and their involvment with the LVA24 engine, I replied as follows and this may be of interest with regard to the above heading. When it was decided that Sulzer would withdraw from the traction market, staff in London and Mantes were naturally very disappointed but had to accept the commercial reasons for such a decision. At this time, Winterthur had designed the A25 engine mainly as a marine auxiliary unit but also for use as main propulsion in river craft and patrol boats etc. This engine was almost identical to the LVA24, so much so that the people at CCM Mantes had pictures of the A25 on the wall marked 'LVA25'! Furthermore, when our engineer Geoff McEwen switched to the Marine division, he knew exactly how this engine worked because of his experience with the 16LVA24 engine in 'Kestrel'.
Winterthur had sold the licence for the LVA24 to English Electric (later Rustons) for traction applications. They didn't build a single engine, but cribbed many of the design features for their RKV series. At the same time, following a very poor experience with the A25 in some locos running in the USA, Winterthur closed down the Traction Division, amalgamated the staff with the Marine Division and we all became the Diesel Division. Thus the French company lost their product and market and became very dispirited. We did try once more with the A25 engine in the UK for the proposed Class 58 loco. BR had called senior staff from companies in the traction industry to attend a seminar in London at which they got us all interested in the prospect of building 750 heavy freight diesel locomotives. However, technical and commercial conditions were completely unacceptable - unlimited rolling guarantees, a series of 100 hour tests without any failures and service engineers at every Works and Depot to administer the guarantees etc. The day Winterthur took the decision to withdraw from tendering due to the contract conditions and cost of testing, I went off to collect some high powered BR technical people from Zurich airport for meetings in Winterthur. It was left to me to explain these decisions over a difficult dinner that evening. Three companies put up solutions for the Class 58 - ourselves, Ruston and Mirrlees - who eventually won the contract, we dropped out, and so did Ruston who breathed a sigh of relief! Mirrlees lost a lot of money on this limited contract (only 60 locos, not 750) and when BR was privatised the freight division renamed EWS Railways, ended up buying American EMD locos!
Kind regards to all those who are still interested in the history of the Sulzer LDA28 engine. Chris Brooks Sulzer 1966 - 1998.
![]()
Highlights of a paper by Mr T Schur of Sulzer Brothers to the Institution of Locomotive Engineeers in 1963.
The paper highlighted problems of design and operation of Sulzer Type 2 & 4 locomotives, which at the time the paper was written had accumulated four years of revenue service.
One item highlighted was the failure of pressure chargers on Type 4 locomotives which were running with the uprated 2,500bhp engine. This failure did not affect the many Sulzer Type 2 & 3 locomotives in service. The pressure charger turbine blades began to shed blades after 8,000 - 12,000 miles of running, with vibration fatigue believed to be the cause. Strain gauge and temperature tests were instituted on turbines of the normal pattern and also on those blades experimentally threaded with damping wire. It was discovered that the temperature at the blade roots was much higher than had been calculated and that although the theoretical blade stress assumed a damping coefficient of 1.8, individual blades were showing a coefficient as low as 1.0. Those blades equipped with damping wires showed no reasonance whatever, it was therefore decided to fit all turbines in service with modified wire-threaded type. Due to the problems of the architechture of the locomotive roof the exchange of pressure chargers was not a simple matter and fifteen months would pass before the replacement program was completed and during that time 10% of the locomotives in service would suffer blade failures.
The uprated engines saw increased peak cylinder pressures which led to difficulties in ensuring a good cylinder head-to-liner gas joint. To overcome this a strengthened head was introduced which would become the standard for replacement of the earlier design. On the new type the mass of metal is concentrated near the joint ring, reducing flexing due to tightening of the holding down nuts. The nuts must be tightened evenly, with the nuts tightened down to the prescribed value, then loosened, then tightened down a second time. This process removes any uneveness and has allowed any heads treated in this way to survive for a whole 'top overhaul' period without blow-by developing.
Excessive cylinder liner wear also became an issue on the Derby built Type 2s, but was not evident with the similarly equipped BRCW Type 2s. At Inverness depot six locomotives of each type were selected to investigate the effectiveness of the air filters. The air filters were weighed when clean, after oiling and again after varied lengths of service. It soon became evident that the lower bodyside filters on the Derby Type 2s collected a large amount of dirt reducing their efficiency as higer proportions of dirt entered the engine room. The BRCW Type 2 filters were mounted at cantrail level and sustained a much lower level of dirt infiltration. This would lead to a redesign of the Derby Type 2 with the air filters being placed at cantrail level.
When built the power units were fitted with magnesium alloy anti-corrosion liners to prevent corrosion in the engine waterways. The liners were cylindrical segments clamped round the cylinder liner. The liners were succesful in preventing corrosion but their longevity was compromised by the quality of water circulating in the engine. The repairs required the entire cylinder liner to be removed, something that was scheduled after six years of service. Since this was way beyond the lifespan of anti-corrosion liners under the then current conditions a program of water treatment was neccesary. These treatments were either sodium chloride or sodium benzoate and sodium nitrate. Soluble oils had been used in other applications but for British Railways this was to be a new experience. Multiple challenges were discovered early in their use: keeping the soluble oil in emulsion form was difficult with engines that had not been previously treated and had rust in the water spaces, the soluble oil also attacked rubber parts such as liner sealing rings not made from nitrile rubber and thirdly the soluble oil quickly showed up weaknesses in joints, particularly at the flat joint between the cylinder block top and the liner flange. In the latter case the top of the block would become distorted in the area of the cylinder head studs. With the problems identified British Railways were successful in implementing soluble oil as a water treatment. Corrosion would still occur until all regions accepted this treatment and that all new engines used the soluble oil treatment continuously from new.
Late in 1955 Sulzer introduced the two-piece, oil-cooled piston, with both scraper rings below the gudgeon pin in order to avoid the stress-raising oil drain holes at the top of the piston, which in previous designs had given trouble. Improvements in oil consumption obtained from placement of a scraper ring placed above the gudgeon pin led to further tests being carried out. These were successful and thought to be caused by an improved piston shape and the material from which it was made. This modification was quickly introduced in bulk on British Railways locomotives. Unfortunately following this modification three engines each less than a year old were discovered with cracked pistons. Investigations revealed that the drain holes above the gudgeon pin were again were the source of the stress raisers. Further investigations revealed it was only the holes immediately above the axis of the gudgeon pin that were responsible, the line of holes in the thrust faces of the piston were not part of the failure. The problematic holes were removed, thus allowing the top scraper ring to remain in place. Oil was now drained through the piston collar into a circumferential collecting gallery, then through the six non-stressed holes and down into the sump.
The new scraper ring position revealed the lubricating oil consumption would be considerably reduced, the new arrangement reduced carbon deposits in the combustion chamber and exhaust system and eliminated the cleaning of these parts as the criterion for overhaul. It was also critical to ensure that these savings in lubricating oil were not neutralised by the quantity of oil used for oil changes. The extension of overhaul periods required an intermediate oil change to be added in between the top overhaul oil changes. At the time the paper was written British Railways were using a low grade lubricating oil. The impurities in this oil led to a by-pass system using cotton waste filters to bring the impuries down to a level which would not harm engines parts. The filters required replacement after 1,500 hours of running, at the time of the paper being written the sludge build up in the Type 4 engines was occuring faster than the filters could remove it.
![]()
Highlights of a paper by S C Holmes from 1969 detailing issues with the 12LDA28 engine.
A discussion of some of the structural failures encountered in BR service
The basic feature of a diesel engine built for traction purposes is that the power to weight ratio should be as high possible bearing in mind such additional details as bulk, transmission arrangements, auxiliaries required, engine life and servicing requirements.
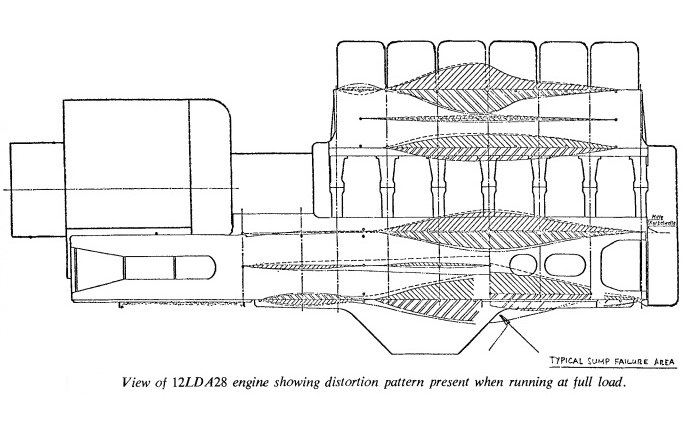
The slow speed 12LDA28 required a large, heavy structure which required a balance between its weight and its strength. Two methods of construction were available, by casting or by welded fabrication, the latter is generally lighter and cheaper than a cast structure. However with the welded structure it is more difficult to avoid points on the structure which will carry a damaging high stress under operating conditions.
Welded fabrication was chosen for the 12LDA28 engine with the crankcase and sump fabricated as one piece and the block as another. An unusual feaure is the engine is essentially two in-line six cylinder engines placed side by side, each with its own crankshaft which were geared to a single output shaft.
The crankcase consists of nine cast steel cross-members which support the seven (for each crankshaft) main bearings and the two (for each gear) coupling gear bearings. These girders are linked by vertical mild steel side walls of double thickness, usually known as box frame girders and a mild steel under-tray which includes a sump.
The crankcase cross-members have upward extensions which meet similar downward extensions from the cast steel cross-members of the cylinder block. The cross-members of the block are linked by solid mild steel sideplates. The top plate of the block is also of mild steel and contains openings for the cylinder liners.
All these items are held together by electric arc welds except that the cylinder block is bolted to the crankcase.
The cylinder heads are separate for each cylinder and are castings, there are two valves in each head. The exhaust gases are used to drive a turbine operated pressure-charger. The traction generator is mounted on rearward extensions of the crankcase box frames.
Operating conditions of the engine
Engines built for traction purposes operate in a challenging environment, with the result that the engines developed unforseen issues as the engines ran up increasing hours and miles. These issues include:
Support Frame for Engine: The main framing of the locomotive cannot be considered completely rigid when the locomotive is moving on uneven track. Unless the deflections of the locomotive body can be totally absorbed in the compliance of the engine mountings, there will tend to be movement of the crankcase. An 'out-of-alignment' error greater than 0.0012 in the crankshaft bearing bores is undesirable from the point of crankshaft fatigue life, this aspect needs careful design. All the 12LDA28 engines on BR have resilient mounting.
External Mechanical Vibration: This is closely connected with the previous point. From work done by the BR Engineering Research Department at Derby, it has been shown that undersirable longitudinal vibrations in the crankshafts of the 12LDA28 engine are much more likely to develop under track conditions than on a static test bed. It is quite probable that there are other shock-induced vibrations in the engine which contribute to damaging stress in the engine structure.
Types of Loads Applied: Under traction service, particularly when working passenger trains the load cycle applied to the engines is challenging. In order to provide sufficient acceleration to maintain a high average speed inspite of service stops and track restrictions, the maximum engine output specified can only be used for short periods, usually less the fifteen minutes. For example on a test of a typical passenger train between Derby & London the engine was running at full power for only 40% of the journey time and the average power output called for during the journey was 50% of the full rated output. Even with a well-designed cooling system and heat exchanger this causes undesirable fluctuations in temperature, particularly in components such as pistons, cylinder heads and cylinder liners. Most of the serious stress appplied to the engine structure will occur at full load, since the duration of full load is only a portion of the engine's life this will be advantageous, though the number of full load cycles in a given service life tend to be indeterminate.
Maintenance and Inspection: Work on most traction equipment is more difficult than on stationary equipment. In particular the examination of an engine when operating at full load is quite difficult if not impossible. Likewise the inspection of a specific engine known to have defective parts may take quite a bit of co-ordination with the operating authorities.
The main types of fracture found on the 12LDA28 engine were as follows:
Crankcase sump:
The sump is welded to the crankcase floor. Developments to the sump have occurred since the engine was introduced on BR, but the principal fracture area has always been the same. The engine structure distorts under load with the most severe distortion occuring in the region of the No.4 cross-member. The corner of the sump where it attaches to the crankcase at the free end coincides with this area and is additionally a considerable distance from the longitudinal neutral axis of the engine. Consequently this area is heavily stressed and any geometrical or metallurgical weak point is likely to initiate a fracture. The weld between the vertical sideplate and the horizontal under-tray at this point provides the weak point and fractures develop in this area. To improve the strength at this point a rolled 'T' section plate was inserted thus removing the weld from the corner.
This issue and several others were also helped by recognising that changes to the out-of-balance forces created by the pistons and the rotating balance weights would reduce a portion of the stresses set up in the engine structure. To reduce these forces three major alterations were made (the percentage in the parentheses indicate the reduction in stress after making the changes):
1/ Reduce the engine speed of the 'C' series from 800rpm to 750 rpm (11%)
2/ Altering the phase angles between the crankshafts (16%)
3/ Increasing the balance weight mass (12.5%)
All three changes were applied to the 'C' series engines, changes 2 & 3 were applied to the 'B' series engines.
Crankcase crossmembers (girders):
A number of fractures occurred in the outer legs of the girders. As well as suffering distortions due to out-of-balance forces this part of the engine structure is in the load path between the cylinder head and crankshaft and stresses of 11 tons per square inch have been measured. Any geometrical stress raiser in the girder may act as an initiation point. Once a fracture has formed , repair is difficult and usually quite a large portion of the girder requires removal. The consequent heat input from the welding process usually results in local distortion and partial remachining of the crankcase is required.
Crankcase Sill Plates:
The crankcase girders have thick horizontal flanges at the level of the crankshaft center line to provide stiffness in the horizontal plane. In the area of the crankcase outer wall these flanges are linked by a series of horizontal sill plates, which are welded to both the girders and the outer wall.
A large number of fractures have begun in the sill plate to girder weld and have propagated into the girder casting. Stresses due to the out-of-balance forces are generally to blame for these fractures, but in the case of the No.7 girder (numbered from the non-drive end) on which a high proportion of fractures are found, there is another reason. The No.7 girder contains the thrust bearings for the crankshafts. At speeds between 600rpm and 700rpm a longitudinal vibration may develop in the crankshafts which transfers to the No.7 member due to the thrust bearing connection, putting stress on the sill plate weld. BR took the option of increasing the longitudinal clearance in the thrust bearings from 0.010 inch to 0.040 inch, thus effectively decoupling the resonant system. Considerable blame for the sill plate fracture position was a result of the quality of welding during the construction of the engines. When efforts were made to to improve the geometry in this area by machining a circular 'scallop' in the corner, it frequently revealed voids and slag inclusions in the welds, which necessitated 'gouging out' and re-welding.
Cylinder Block Side Plate Welds:
When discussing cylinder block fractures a further factor is introduced on all fractures which originate inside the water jacket: the effect of coolant on any weak spots in the structure. Initially the Sulzer engines on the LMR used untreated water as coolant, leading to higher rates of corrosion until suitably treated water was substituted. Additionally the poor quality of some butt-welded joints gave problems. Instead of a substantially flat flush surface a notch was left leading to accelerated corrosion with the resulting reduced cross-section, leading to high stress and eventual failure. The side plate welds also lay in the load path between the cylinder head and the crankshaft.
Cylinder Block End Casting:
This situation was similar to the sideplate weld except the position was worsened by surface faults in the cast steel endplate, in bad cases the upper part of the endplate was replaced with a mild steel plate.
Cylinder Block Internal Water Pipe Manifold:
This is a steel pipe which runs the length of the block along its centerline and distributes the coolant to the block. It is threaded through the block crossmembers and also forms part of the 'floor' of the water jacket. Distortion of the engine when running puts a high stress on the fillet welds between the pipe and the cross members, fractures which initiate in the weld eventually propagate into the pipe. If this happens on the lower side of the pipe, coolant will leak into the crankcase and contaminate the engine oil. Usually the fracture is due to a badly shaped weld fillet, sometimes with welding faults. Corrosion also explains the incidence of failures, in a typical period there were 57 fractures on the oil side and 474 fractures on the water side. The reduction of out-of-balance forces and improvement in fillet weld profiles (convex to concave) have contributed to the reduction in fractures in this area.
Fractures in the underside of the Fuel Pump Tray:
Fractures begin in the corner of the fillet weld holding the fuel pump tray down onto the block crossmember. This area is on the edge of the gas force load path and is high stressed. Once the fracture has started it tends to spread into the cross member. Any lack of quality in the weld or weld profile in this highly stressed area will result in the fracture starting.
In summary, the use of welded construction for the 12LDA28 engine may have initially provided an economic incentive over cast construction, but was that lost as the engines started to reveal their weaknesses over time?
Page added February 17th 2014
Last updated September 13th 2024